Trust Basics
What is a Trust?
A trust is a legal entity that holds assets for the benefit of another. Basically, it’s like a container that holds money or property for somebody else.
There are three parties in a trust arrangement:
- The grantor (also called a settlor or trustor): This is the person who creates and funds the trust.
- The beneficiary: This is the person or people who receive benefits from the trust, such as income or the right to use a home and have what is called an equitable title to trust property.
- The trustee: This is the person or people who hold legal title to trust property, administer the trust, and have a duty to act in the best interest of the beneficiary.
You create a trust by executing a legal document called a trust agreement. The trust agreement names the beneficiary and trustee. It also contains instructions about what benefits the beneficiary will receive, what the trustee’s duties are, and when the trust will end, among other things.
Funding a Trust
You can put almost any kind of asset into a trust, including cash, stocks, bonds, insurance policies, real estate, and artwork. The assets you choose to put in a trust will depend largely on your goals. For example, if you want the trust to generate income, you could put income-producing assets, such as bonds, in your trust. If you want your trust to create a fund that can be used to pay any estate taxes due after your death or to provide for your family when you die, you might fund the trust with a life insurance policy.
Potential Advantages
A trust can:
- Help reduce estate taxes;
- Shield assets from potential creditors;
- Avoid the expense and delay of probate*;
- Preserve assets for your children until they are grown, in case you should die while they are still minors;
- Create a pool of investments that can be managed by professional money managers;
- Set up a fund for your own support in the event of incapacity;
- Shift part of your income tax burden to beneficiaries in lower tax brackets; and
- Provide benefits for charity.
*Note: Probate is the court-supervised process of settling a deceased person’s estate. Probate can be a complicated process and often takes six to eighteen months to complete.
Potential Considerations
However, trusts also have potential disadvantages. First, there are costs associated with setting up and maintaining a trust. These may include trustee fees, professional fees, and filing fees. It’s also important to know that, depending on the type of trust you choose, you may give up some control over the assets in the trust. Also, maintaining the trust and complying with recording and notice requirements can take considerable time. Lastly, income generated by trust assets and not distributed to trust beneficiaries may be taxed at a higher income tax rate than your individual rate.
Types of Trusts
There are many types of trusts, the most basic being revocable and irrevocable. The type of trust you should use will depend on what you’re trying to accomplish.
Living (Revocable) Trust
A living trust is a trust that you create while you’re alive. A living trust:
- Avoids probate. Unlike property that passes to heirs by your will, property that passes by a living trust is not subject to probate, avoiding the delay of property transfers to your heirs and keeping matters private.
- Maintains control. You can change the beneficiary, the trustee, and any of the trust terms as you wish. You can also move property in or out of the trust, or even end the trust and get your property back at any time.
- Protects against incapacity. If, because of an illness or injury, you can no longer handle your financial affairs, a successor trustee can step in and manage the trust property for you while you get better. In the absence of a living trust or other arrangement, your family may have to ask the court to appoint a guardian to manage your property.
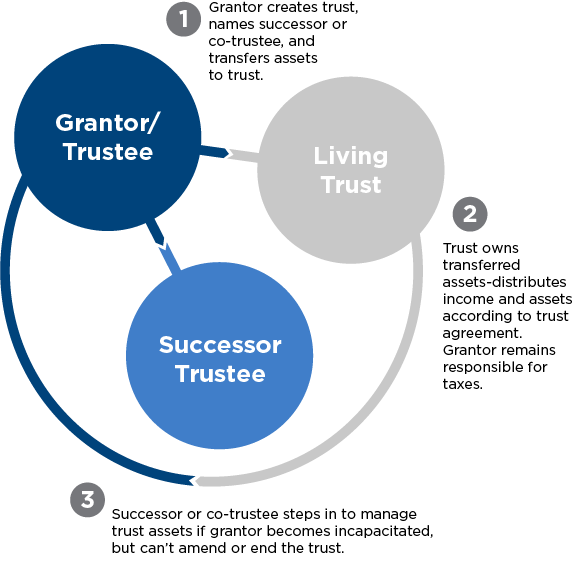
A living trust can also continue after your death. You can direct the trustee to hold trust property until the beneficiary reaches a certain age or gets married, for instance.
Despite these benefits, living trusts have some drawbacks. Property in a living trust is generally not protected from creditors, and you cannot avoid estate taxes using a living trust.
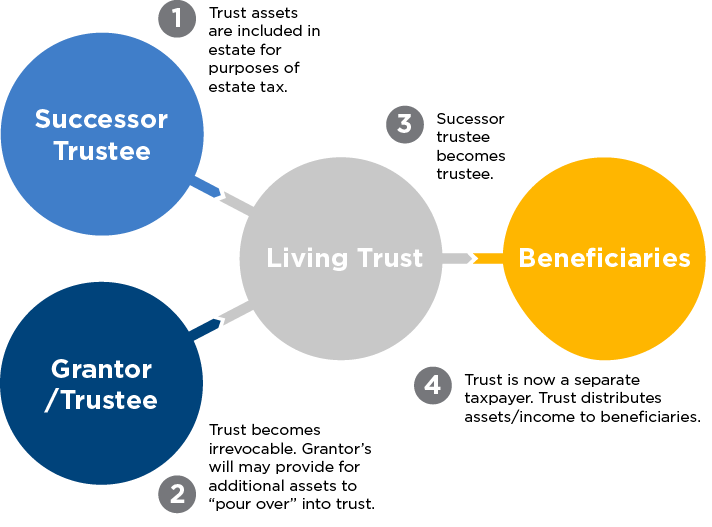
Irrevocable Trusts
Unlike a revocable trust, you can’t easily change or revoke an irrevocable trust. Also, for this type of trust, you usually cannot change beneficiaries or change the terms. Irrevocable trusts are frequently used to help reduce potential estate taxes. The transfer may be subject to gift tax at the time when property is transferred into the trust, but the property, plus any future appreciation, is usually removed from your gross estate.
Additionally, property transferred through an irrevocable trust will avoid probate and may be protected from future creditors.
For help deciding which type of trust might best fit your needs and goals, call CAPTRUST.